Java多线程编程中,有时候在线程的run方法中,我们使用死循环来处理我们的任务,在不控制的情况下线程会一直执行,无法退出。因此在主线程中需要一些方式控制线程退出。
在Java的多线程编程中有3种方式退出线程:
- 使用线程的stop方法(不推荐)。
- 使用退出标志位。
- 使用Interrupt() 方法退出线程。(推荐)
下面就这三种方法做一些简要的讲解和使用。
使用线程的stop方法(不推荐)
使用该方法就像运行中的计算机突然停电,它是不安全的,而且该方法已被弃用,最好不要使用它。
线程的stop方法会抛出一个ThreadDeatherror的错误,并且会释放子线程所持有的所有锁,这样会导致数据的不一致性。
例子:
class ThreadTask extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println(this.getName() + "run task ");
}
}
}
public class ThreadStopExample extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
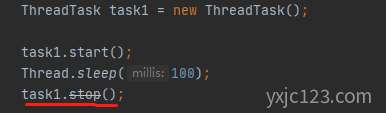
ThreadTask task1 = new ThreadTask();
task1.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
task1.stop();
}
} 我们在Idea中stop()代码行也是一个删除线,说明该方法是弃用的。
使用退出标志位。
使用该方法的方式是在线程类中定义一个标志位如:isExist,通过该标志位判断循环是否继续执行。
class ThreadTask extends Thread{
private volatile Boolean isExit = false;
public void setIsExit(Boolean isExit) {
this.isExit = isExit;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(!isExit){
//处理一些任务
System.out.println(this.getName() + "run task ");
}
}
}
public class ThreadStopFlagExample extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadTask task1 = new ThreadTask();
task1.start();
Thread.sleep(1);
//设置退出标志
task1.setIsExit(true);
}
} 在上面的例子中,我们sleep(1)后,修改子线程的标志位isExit让线程退出。
使用Interrupt() 方法退出线程。(推荐)
interrupt() 方法是中断线程,它是通知目标线程退出,并不是立即退出,也就是说,线程内部也得用某个方法( Thread.isInterrupted() )判断是否需要退出,当然你可以拒绝。
例子:
class ThreadTask extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//判断是否发送了中断
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
System.out.println(this.getName() + "run task ");
}
}
}
public class ThreadStopInterruptExample extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadTask task1 = new ThreadTask();
task1.start();
Thread.sleep(10);
//发送中断信号
task1.interrupt();
}
} 上面的代码中我们通过Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()方法判断是否需要退出,它和标志位有点类似。
我们再看一个在线程内部 while循环中使用sleep方法的例子:
class ThreadTask extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//判断是否发送了中断
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//内部使用了sleep方法
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(this.getName() + "run task ");
}
}
}
public class ThreadStopInterruptSleepExample extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadTask task1 = new ThreadTask();
task1.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
//发送中断信号
task1.interrupt();
}
}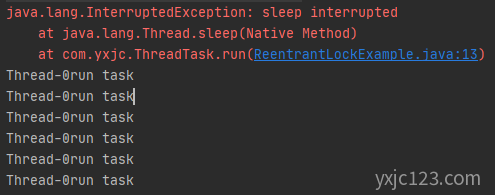
所以这个时候需要将上述在sleep catch代码块中退出线程即可,修改后的代码如下:
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;//捕获到异常,跳出循环
}